Immune System Blood Test
The past two to three years has provided us with an opportunity to learn all about our immune system. Conceptually, we talk about it all the time. But what is it? And how do you test it to see if yours is strong or not?
The Immune System is made up of cells, tissues, organs and substances that help the body fight infections and other diseases. It includes white blood cells and organs and tissues of the lymph system, such as the thymus, spleen, tonsils, lymph nodes, lymph vessels, and bone marrow. Vitamins and trace minerals play a role regulating its functioning.
The Immune System Panel is designed to let you know how you might respond to various viruses or infectious diseases, including Covid and the flu.
This panel includes:
Vitamin D
C-Reactive Protein: CRP
IL-6: Interleukin-6
CBC: Complete Blood Count
Zinc, Serum
Read on below to learn more about the individual tests.
Call the office to set up an appointment or order bloodwork. I am available to see patients virtually with Telemedicine or in person. Office number 404-320-0204
If you are interested in learning about supplements that will support your immune system, read the article here.
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Complete Blood Count is a panel that includes 15 individual tests. It lets us know if you have an infection, acute or chronic, viral or bacterial or anemia. Often we can then address this with supplementation
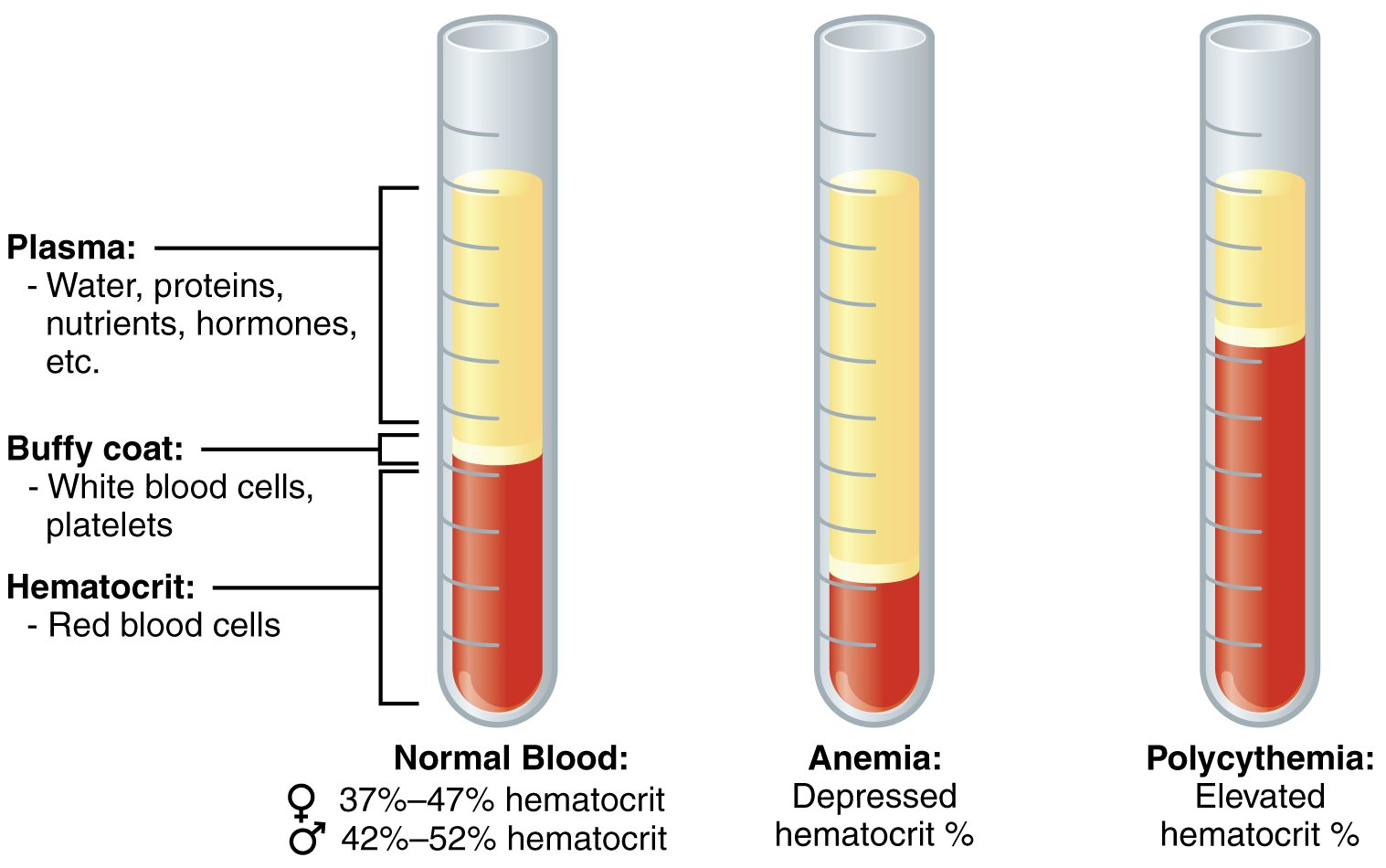
For example, one test is called the Hematocrit. This tests the measurement of how much of your blood is made up of red blood. Also used for anemia and other disorders. The graphic below shows what makes up your blood and what varying hematocrit levels will show.
Complete Blood Count (CBC) with Differential and Platelet tests for:
White Blood Count - Fights infection. Tests for different kinds of white blood cells including Polys (SEGS-PMNS), Lymphocytes, Monocytes, Eosinophils, Basophils, and Immature Granulocytes
Red Blood Count - Carries oxygen from your lungs to the rest of your body. Tests the actual number of red blood cells in your blood sample
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV) is a measurement of the average size of your red blood cells.
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) is a calculated measurement of the average amount of hemoglobin inside your red blood cells.
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) is a calculated measurement of the average concentration of hemoglobin inside your red blood cells.
Red cell distribution width (RDW) is a measurement of the variation in the size of your red blood cells.
Hemoglobin - The protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen from your lungs and to the rest of your body - often used to check for anemia
Hematocrit - Tests the measurement of how much of your blood is made up of red blood. Also used for anemia and other disorders.
Platelets - Helps your blood to clot and stop bleeding. Measures the average number in blood.
Lymphocytes- A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell. They include natural killer cells, T cells, and B cells. They are the main type of cell found in lymph.
Monocytes- A type of white blood cell made in the bone marrow and can influence your immune response and tissue repair
Eosinophils- white blood cells that help alert the body of infection and helps modulate some parasites
Basophils- a type of white blood cell that detects and destroys some early cancer cells. It also releases histamine in an allergic reaction or an asthma attack.
Neutrophils/Polys- also white blood cells that kill infection and heal damaged tissue
Immature Granulocytes- are white blood cells that are immature.
Zinc, Serum
Zinc Is a trace mineral and is involved in creation of DNA, growth of cells, building proteins, healing damaged tissue, and supporting a healthy immune system.
Zinc is a cofactor in more than 300 enzymes that impact different organ functions, playing role in immune function. A cofactor is something, a catalyst, that makes enzymes function.
“It is clear that this trace element has a broad impact on key immunity mediators, such as enzymes, thymic peptides and cytokines, explaining the paramount importance of zinc's status on the regulation of lymphoid cell activation, proliferation and apoptosis.” Source Pubmed
Interleukin- 6
Interleukin-6 is one of a large group of molecules called cytokines. Cytokines are proteins that help with signaling. With the immune system, they help direct the body’s immune response. They are a part of the “inflammatory cascade” that involves the coordinated, sequential activation of immune response pathways.
Because Il-6 helps regulate immune responses, the test is a useful as a marker of immune system activation. IL-6 can be elevated with inflammation, infection, autoimmune disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and some cancers.
“IL-6 test results measure the amount of IL-6 circulating in the blood, and are used as one sign of systemic inflammation.
A normal level of IL-6 may represent people who do not have an infection or inflammation.
A low level of IL-6 may be expected for most patients with a less severe inflammatory response.
A high level of IL-6 may be one sign that the inflammation is severe and could lead to complications.” -Labcorp
C-Reactive Protein: CRP
CRP is a protein made by the liver and levels increase when there’s inflammation in the body.
If levels of CRP are high in the body, we are able to create a plan to reduce inflammation through proper supplementation along with diet and lifestyle shifts.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D has shown antimicrobial & anti-inflammatory properties
Yes, Vitamin D is responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate. But wait!! There’s more.
Almost all immune cells have a Vitamin D receptor. Vitamin D therefore has the ability to modulate (regulate) the immune system. “Deficiency in vitamin D is associated with increased autoimmunity as well as an increased susceptibility to infection.”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3166406/
It is almost impossible to get enough Vitamin D in contemporary living. Knowing your level and supplementing accordingly is paramount to your health.